Divided Destinies: The Unresolved Armenia-Azerbaijan Land Conflict
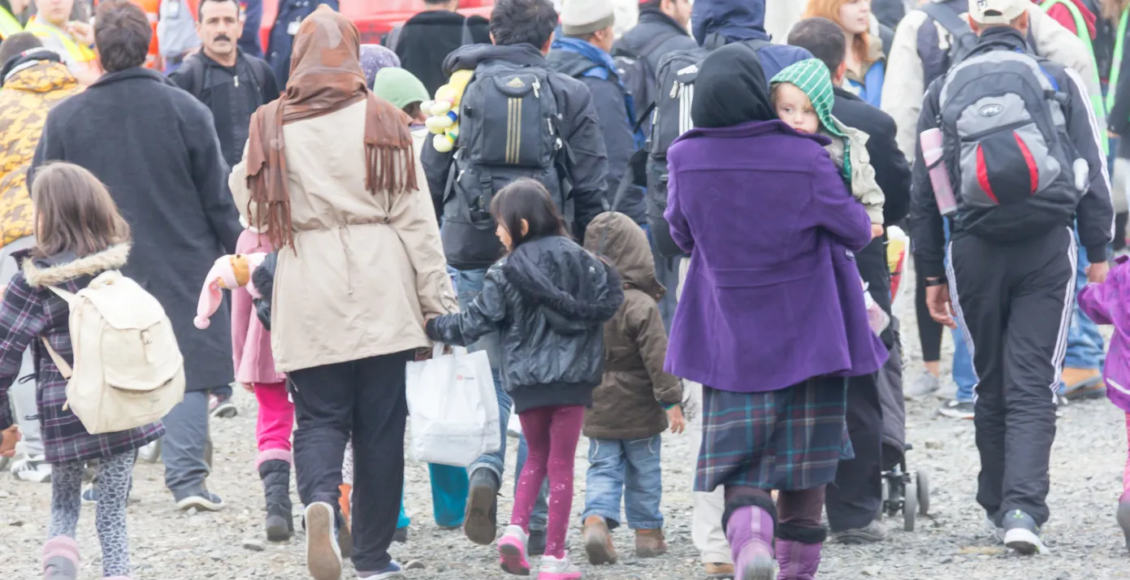

In the heart of the South Caucasus, a simmering conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan has recently flared up with ever-more intensity, casting a spotlight on a long-standing territorial dispute over the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The historical animosity between the two nations has once again manifested itself in brutal military confrontations, with Baku ultimately reclaiming control over the contested region. As these two countries grapple with the unfolding scenario, the ripple effects are being felt far beyond their borders, drawing the eyes of the world towards the Armenia-Azerbaijan dispute.
Legacy Of Discontent
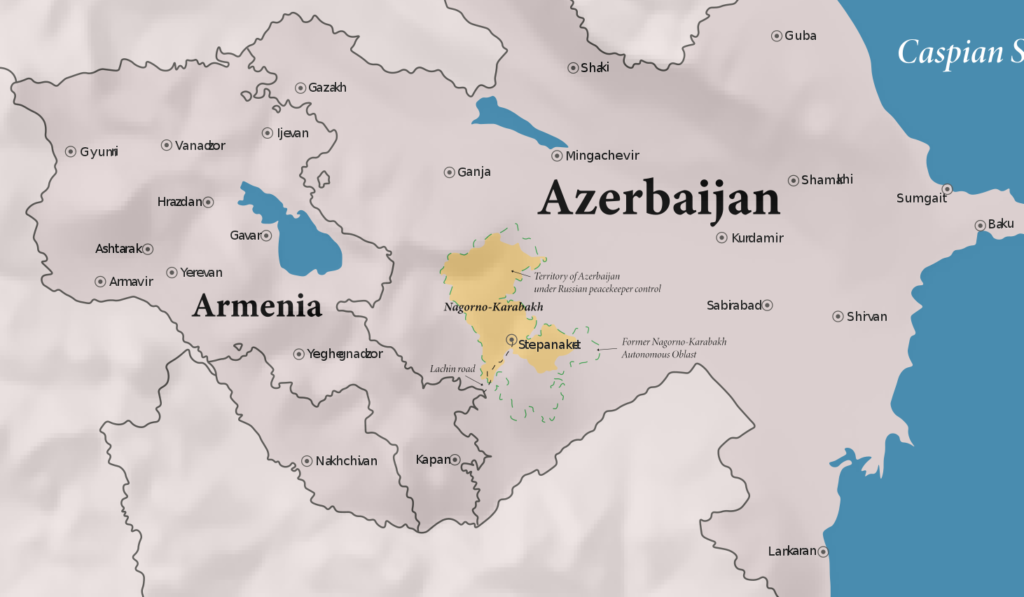
The roots of the Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict trace back to the early 20th century when both nations, under the Soviet Union, laid competing claims to Nagorno-Karabakh, a region inhabited by a majority of ethnic Armenians but assigned to the Azerbaijani Soviet Socialist Republic by Soviet authorities. The simmering tensions persisted throughout the Cold War era and exploded into open conflict as the USSR dissolved.
The early 1990s saw the escalation into a full-fledged war over Nagorno-Karabakh, ending in a ceasefire in 1994, with ethnic Armenians gaining de facto control over the region but Azerbaijan retaining de jure control. Nevertheless, the truce did not resolve the underlying territorial dispute, and occasional confrontations continued over the years. The conflict reignited in 2020 with a 44-day war, which resulted in significant casualties and displacement of ethnic Armenians from Artsakh (Nagorno Karabakh), yet again highlighting the volatility of the situation and the enduring grievances that fuel the conflict.
The year 2023 bore witness to a marked escalation in the dispute, with Azerbaijan initiating a military offensive in September, to not only regain control over the disputed territory but also enforce a complete withdrawal of Armenian forces from the region. The aftermath of this attack unfolded a humanitarian crisis with almost 99.9% of ethnic Armenians, finding themselves amidst an exigent exodus, fleeing the renewed hostilities in search of refuge back in Armenia. Moreover, the capture of Nagorno-Karabakh exacerbated the situation, with the fleeing populace leaving behind a region now grappling with the scars of conflict. The stories of those who left in haste echo through the deserted towns and villages, rendering the region a poignant emblem of the larger Armenia-Azerbaijan discord.
The impacts of the conflict are enormous. Armenian society is confronting enduring economic upheaval, tangible and perceived risks of continued hostility, and uncertainty surrounding the nation’s prospects. Armenian citizens are expressing their discontent and fears about the future of the region since the separatist authorities, grappling with the onslaught, announced the dissolution of the ethnic Armenian enclave, scheduled for January 1, 2024. Moreover, a report highlighted the aggravating factors that could potentially deepen the crisis in Armenia, emphasizing the need for humanitarian assistance and a renewed focus on ensuring the safety and well-being of the affected populations.
The Response of the International Community
The unfolding situation has garnered a significant response from the international community and notably the European Union (EU). They have taken a prominent role in mediating negotiations between Armenia and Azerbaijan, showing their commitment to work alongside both nations. In order to overcome tensions and pave the way for a stable and peaceful South Caucasus, they invited leaders of both countries to establish a consensus, underscoring the urgency of diplomatic dialogues. On the humanitarian front, the EU has boosted aid to Armenia, acknowledging the significant population displacement and economic turmoil.
France, with its historically strong ties with Armenia, has taken a more active role by providing military aid, demonstrating tangible support that goes beyond diplomatic overtures. Consequently, the Azerbaijani president Ilham Aliyev has voiced strong criticism towards Macron, accusing him of exacerbating tensions in the region rather than fostering a peaceful resolution of conflict. Nonetheless, France has emphasized its commitment to preserving Armenia’s territorial integrity.
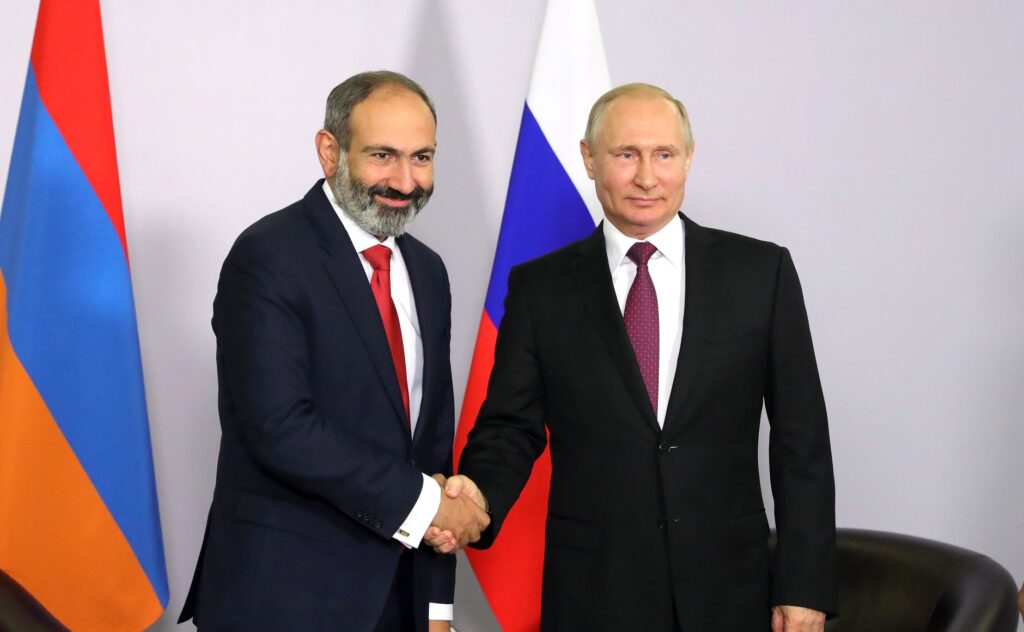
The conflict also strained Armenia-Russia relations, marked by many centuries of close political and military ties, which have been vital for Armenia’s’ security. Russia claims to provide security to Armenia through the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), a military alliance of post-Soviet states that doesn’t include Azerbaijan. However, recent events have led Armenian officials to question the reliability of Russia as a security partner, especially against the backdrop of Moscow’s inaction to Azerbaijani “aggression” and the degradation of the Russian army in Ukraine.

Beyond The Battlefield
The persisting tensions in the region depict a fragile regional milieu that demands urgent international mediation to thwart further escalations. The discord has destabilized the stability of the South Caucasus and could potentially strain international relations. As such, the proactive engagement of international bodies like the EU is imperative to mitigate the repercussions of the conflict and pave the way for a sustainable resolution.
Edited by Joseph Pappas.
Featured Image: “Ethnic Armenians flee their homes in Nagorno-Karabakh” by Raimond Spekking is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 DEED.
